life cycle of a seedless plant
We have a new and improved read on this topic. The seedless vascular plants go through an alternation of generations just as the nonvascular plants and other vascular plants do.

Pin By Dandavats Dasa Flores On Botany Fern Life Cycle Life Cycles Rhizome
We have a new and improved read on this topic.

. Key Points The life cycle of seedless vascular plants alternates between a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte phase. The dominant part of the fern life cycle is the diploid sporophyte generation - those are the large plants that are obvious. Non-vascular plants require water to thrive because they dont have the means to retain water on their own.
However not all plants produce seed. Seedless plants produce spores instead of seeds and they can be vascular meaning they retain water in the tissue of the plant or they can be non-vascular. The dominant phase of the life cycle is the diploid sporophyte while the gametophyte is a small but self-sufficient creature.
For this reason sexual reproduction must happen in the presence of water. Transported by wind or water. The male gametophyte produces flagellated sperm that must swim to the egg formed by the female gametophyte.
Live worksheets English Science Plant reproduction Life cycle of seedless plant. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants. Seedless vascular plants have a generational cycle in which the diploid sporophyte phase alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase.
Describes the life cycle of seedless vascular plants. Spores germinate forming a hapliod gametophyte. In seedless vascular plants the sporophyte became the dominant phase of the lifecycle.
Life Cycle of Seedless Vascular Plants. The undersides of the leaves are dotted with clusters of sporangia. The life cycle of nonvascular seedless plants can be described as follows.
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. Recall the sporophytic generation is the diploid part of the life cycle and via meiosis haploid spores are produced. Zygote first cell formed from the fertilization of an egg cell with a sperm cell.
- produce gametesn through the process of mitosis. In seedless vascular plants the diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the lifecycle. Students will know the different parts of a fern.
This then grows into a sporophyte. The spores develop into tiny separate gametophytes from which the next generation of sporophyte plants grows. Water is still required for fertilization of seedless vascular plants and most favor a moist environment.
Students will learn the life cycle and reproduction of a plant. Like all plants seedless vascular plants have a gametophytic generation and a sporophytic generation. One gametophyte produces sperm cells that fertilize the egg cells of another gametophyte forming a zygote.
- sperm cells are transported by water to egg cells. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants is an alternation of generations where the diploid sporophyte alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase. Non-vascular seedless plants include mosses hornworts and liverworts.
Seedless vascular plants require water for. Gametophytes of seedless plants. When spores land they grow into gametophytes.
Pteridophytes ferns are the seedless vascular plants. The plants in Division Pteridophyta are seedless. The life cycle pattern in both Pteridophyta and Spermatophyta is basically same.
They have an alternation of generations not unlike the bryophytes the seedless nonvascular plants. Pteridophyta reproduces through spores since they are flowerless and seedless. Remember that the moss life cycle is characterized by two types of haploid spores male and female.
Students will be able to recognize the fern life cycle. Describes the life cycles of seedless vascular plants. During the life cycle of a seedless plant a sporophyte releases.
Throughout plant evolution there is an evident reversal of roles in the dominant phase of the lifecycle. Seedless vascular plants reproduce through unicellular haploid spores instead of seeds. The gametophyte is now an inconspicuous but still independent organism.
Seedless vascular plants also have a haploid gametophyte generation but it is independent and reduced in size compared to nonvascular plants. During the life cycle of a seedless plant sporophyte releases when spore land they grow into gametophytes. Students will understand why a fern is a seedless vascular plant.
The plants in Division Pteridophyta are seedless. Answered 6 years ago Author has 547 answers and 7665K answer views. Small plants generally lacking vascular tissue specialized cells for the transport of material although water-conducting tubes are present in some mosses may be unrelated to vascular tissue life cyclegametophyte dominant unlike other plants.
Key Points The life cycle of seedless vascular plants alternates between a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte phase. These do not multiply by seeds as the plants in Division Spermatophyta. The lightweight spores allow.
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. The gametophyte is now an inconspicuous but still independent organism. Modern-day seedless vascular plants include club mosses horsetails ferns.

Ferns An Ecological Manual Of New York City Plants In Natural Areas Fern Life Cycle Life Cycles Ferns

Western Sword Fern Life Cycle C Don Boucher Vegetal Biologia Plantas Jardin

Classifications Of Flowering And Non Flowering Plants Plant Classification Biology Plants Teaching Plants

Life Cycle Of The Fern Candace Jordan Class Plant Life Cycle Ferns Fern Life Cycle

Lab Ch 16 Non Vascular Plants And Seedless Vascular Plants Biology 152 With Kinnes At Azusa Pacific University Studyblue Vascular Plant Plants Vascular

4 Gb2 Learnres Web 06plan Plants Vascular Plant Gymnosperm

Fern Plants And Their Life Cycle Seedless Vascular Updated Plants Fern Plant Vascular Plant

Department Of Botany Botany Biology Plants

Moss Life Cycle Life Cycles Biology Plants Biology Projects

Https Session Masteringbiology Com Myct Itemview Offset Next Meiosis Mitosis Egg Forms

Bryophyta Moss Life Cycle Life Cycles Biology Plants Biology Projects

Types Of Plants Classifying Plants Types Of Plants Plants

The Open Door Web Site Colonizing And Populating Habitats Seeds And Spores The Pteridophytes Ferns And Horsetails Biology Plants Fern Life Cycle Spore
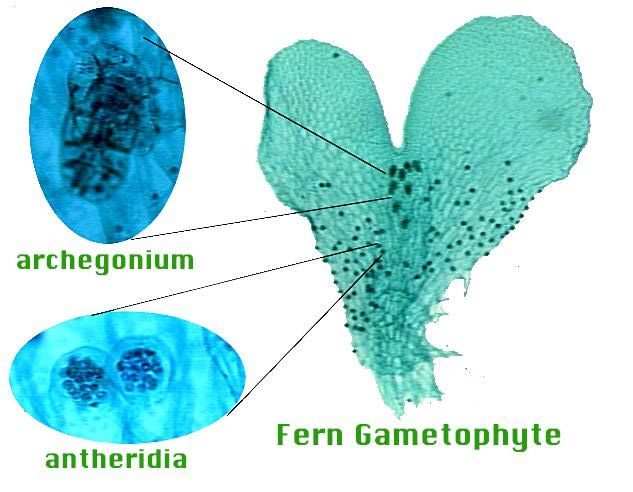
Page Not Found Uroki Biologii Biologiya Botanika

The Surprising Way Ferns Reproduce Fern Life Cycle Ferns Plants

Plants Ii Non Vascular And Seedless Vascular Plants Biol110f2012 Confluence Vascular Plant Vascular Plants

Life Cycle Of The Fern Kidspressmagazine Com Fern Life Cycle Life Cycles Life Cycle Stages

